4 Web Services and APIs
4.1 Introduction
The terms “web services” and “APIs” are often used interchangeably, but they are not the same. Although both are software components used to facilitate communication between different systems and applications, understanding their differences of these tools is essential to use them effectively. A web service is a software system designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction over a network. An API, or Application Programming Interface, is a set of rules and protocols that allow one software application to interact with another. An API can be used to access the functionality of a web service, but it can also be used to access the functionality of a library or other software component.
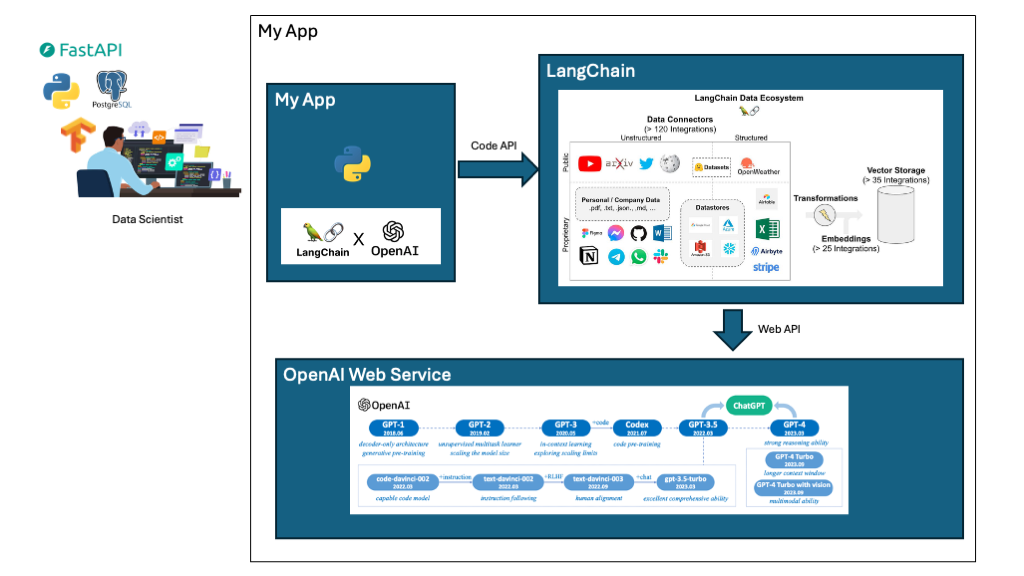
As a data science or ML engineer, you will likely need to interact with web services and APIs to access data, models, and other resources in your daily job. You may not realize it, but APIs and web services are everywhere, and you’re probably using them right now without noticing. For example, in the cutting-edge era of large language models (LLMs), companies such as OpenAI and Google have their own exclusive foundation models. Although these models do not offer direct access to their implementations or code for various reasons, they provide APIs that enable access to the powerful capabilities of their LLM models. By skillfully integrating these features into our applications, we can significantly enhance their functionality. The following diagram clearly depicts the seamless interplay between a web service and an API.